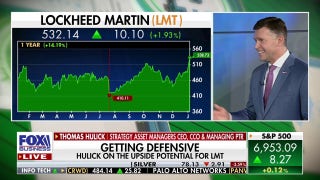
Coronavirus lives on surfaces for up to 3 days, says new test
The virus has shown it can live longer than previously expected
The new coronavirus can live in the air for several hours and on some surfaces for as long as two to three days, tests by the U.S. government and other scientists have found.
Their work, published Wednesday, suggests people can get infected through the air as well as from touching things that were contaminated by others who have it, in addition to direct person-to-person contact.
WHERE CAN YOU GET A CORONAVIRUS TEST?

An employee disinfects the glass cover of a butcher counter to prevent the spread of the novel coronavirus in a food store in Budapest, Hungary, Wednesday, March 11, 2020. (Tamas Kovacs/MTI via AP)
Since emerging in China late last year, the new virus has infected more than 120,000 people worldwide and caused more than 4,300 deaths -- far more than the 2003 SARS outbreak caused by a genetically similar virus.
For this study, researchers used a nebulizer device to put samples of the new virus into the air, imitating what might happen if an infected person coughed or made the virus airborne some other way.
They found that viable virus could be detected up to three hours later in the air, up to four hours on copper, up to 24 hours on cardboard and up to two to three days on plastic and stainless steel.
Similar results were obtained from tests they did on the virus that caused the 2003 SARS outbreak, so differences in durability of the viruses do not account for how much more widely the new one has spread, researchers say.

A worker in a protective suit sprays disinfectants at a school that has suspended classes in San Juan city, east of Manila, Philippines, on Monday, March 9, 2020. (AP Photo/Aaron Favila)
The tests were done by scientists from the National Institutes of Health, Princeton University and the University of California, Los Angeles, with funding from the U.S. government and the National Science Foundation.
GET FOX BUSINESS ON THE GO BY CLICKING HERE
The findings have not been reviewed by other scientists yet and were posted on a site where researchers can quickly share their work before publication.
“It’s a solid piece of work that answers questions people have been asking,” and shows the value and importance of the hygiene advice that public health officials have been stressing, said Julie Fischer, a microbiology professor at Georgetown University.
“What we need to be doing is washing our hands, being aware that people who are infected may be contaminating surfaces,” and keeping hands away from the face, she said.
CLICK HERE TO READ MORE ON FOX BUSINESS
___
Marilynn Marchione can be followed on Twitter: @MMarchioneAP
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education. The AP is solely responsible for all content.