Oregon high court keeps state coronavirus restrictions in place
The decision kept statewide virus restrictions in place by halting a judge’s order to end them.
Get all the latest news on coronavirus and more delivered daily to your inbox. Sign up here.
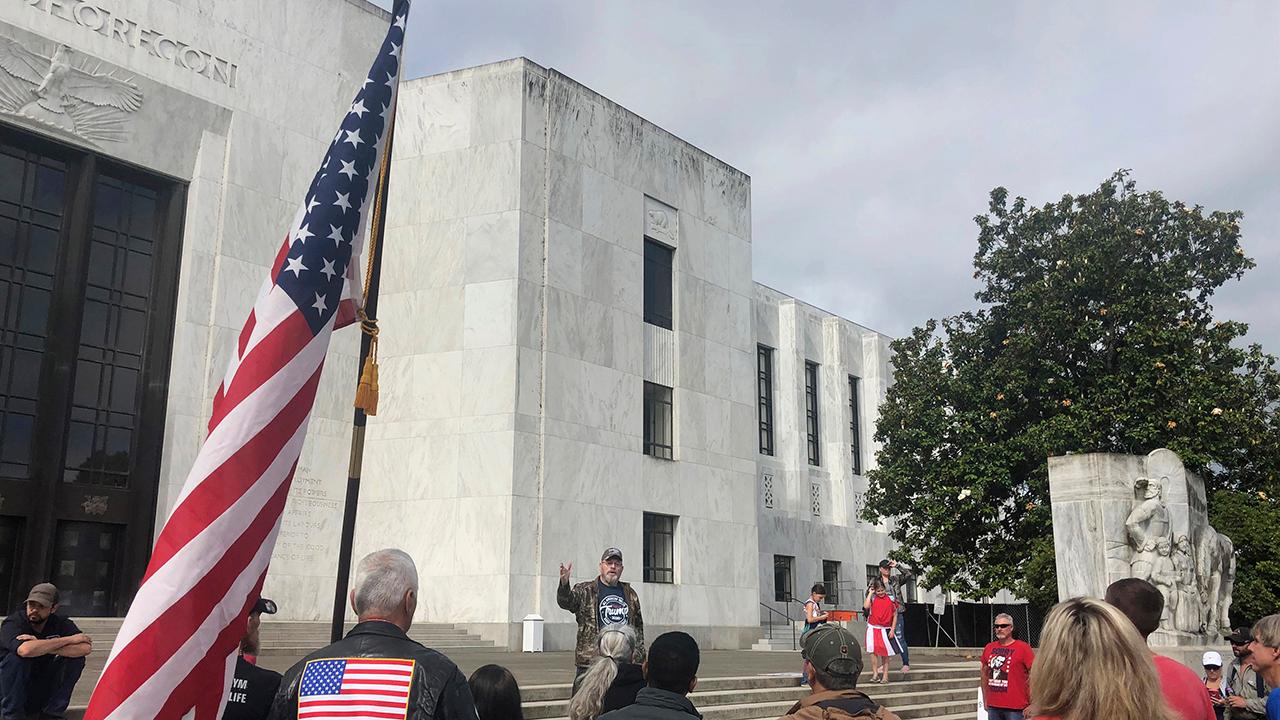
The Oregon Supreme Court has kept statewide coronavirus restrictions in place by halting a judge’s order to end them in a lawsuit claiming the governor exceeded her authority when she shut down in-person religious services.
Baker County Circuit Judge Matthew Shirtcliff ruled Monday that Gov. Kate Brown erred by not seeking the Legislature’s approval to extend her stay-at-home orders beyond a 28-day limit. Brown’s lawyers appealed to the Oregon Supreme Court, which just hours later put a hold on Shirtcliff’s decree until the high court’s justices can review the matter.
Presiding Justice Thomas Balmer gave both sides until Friday to submit legal briefs. He did not give a timeline for a decision.
The lower court judge had issued his opinion in response to a lawsuit filed earlier this month by 10 churches around Oregon that argued the state’s social distancing directives were unconstitutional.
In a statement late Monday, Brown, a Democrat, praised the state Supreme Court action.
“There are no shortcuts for us to return to life as it was before this pandemic. Moving too quickly could return Oregon to the early days of this crisis, when we braced ourselves for hospitals to be overfilled,” she said.
Kevin Mannix, an attorney representing businesses in the case, said Tuesday that he was encouraged that the state Supreme Court seemed to be taking the case seriously. Normally, briefings in cases before the court wouldn’t be due until June 1, he said.
OREGON STRIP CLUB BRINGS BURLESQUE TO CORONAVIRUS CARRY-OUT
“Every day that the governor’s order remains in effect, people are prevented from being able to assemble peaceably, their free expression rights are limited … and most significantly, their freedom of religion rights are restricted,” he said. “This extraordinary power that she’s been exercising has a time limit on it.”
In his opinion, Shirtcliff wrote that the damage to Oregonians and their livelihood was greater than the dangers presented by the coronavirus. He also noted that other businesses deemed essential, such as grocery stores, had been allowed to remain open even with large numbers of people present and have relied on masks, social distancing and other measures to protect the public.
“The governor’s orders are not required for public safety when plaintiffs can continue to utilize social distancing and safety protocols at larger gatherings involving spiritual worship,” he wrote.
Courts in other states have ruled against similar orders. The Wisconsin Supreme Court struck down Gov. Tony Evers’ stay-at-home order last week, ruling that his administration overstepped its authority when it extended the order for another month without consulting legislators.
A federal judge in North Carolina on Saturday sided with conservative Christian leaders and blocked the enforcement of restrictions that Gov. Roy Cooper ordered affecting indoor religious services during the pandemic.
The order from Judge James C. Dever III came days after two churches, a minister and a Christian revival group filed a federal lawsuit seeking to immediately block enforcement of rules covering religious services within the Democratic governor’s executive orders.
In Louisiana, however, a federal judge refused a minister’s request to temporarily halt Gov. John Bel Edwards’ stay-at-home order, which expired that same day.
LIMITED BY CORONAVIRUS RESTRICTIONS, SUPREME COURT HOLDS FIRST-EVER TELECONFERENCED ARGUMENTS
The ruling by the county judge in Oregon turned on the legal mechanism Brown used to issue her orders. The plaintiffs allege — and the judge agreed — that they were issued under a statute pertaining to public health emergencies, not an older provision that addresses natural disasters such as storms, earthquakes or floods.
The public health statute contains the 28-day time limit, while the other would give Brown broader powers but is not relevant in the current situation, said Kevin Mannix, who is representing business owners in the case.
California, Washington state and New York — where governors have repeatedly extended coronavirus restrictions — give their governors more power in public health emergencies, but Oregon law puts a specific clock on those “extraordinary powers,” he said.
“Maybe other states will take a lesson from us in the future about what to do about public health emergencies,” Mannix said. “We’ve thought about it, we’ve balanced the powers of the governor with the powers of the people and their representatives.”
Brown declared a statewide state of emergency due to the virus on March 8 and has issued multiple executive orders since then, including the closure of all schools, nonessential businesses and a ban on dine-in service at restaurants and bars.
Earlier this month, Brown extended the order another 60 days until July 6. All but a handful of Oregon counties, however, got the state’s approval to begin loosening those restrictions last Friday.
Also Tuesday in a separate case, a federal judge denied an emergency injunction on Brown’s stay-at-home orders sought by a coalition of nine businesses and one nonprofit. The Oregonian/OregonLive reports that U.S. District Judge Michael J. McShane found the plaintiffs were unlikely to succeed on their federal constitutional claims.
GET FOX BUSINESS ON THE GO BY CLICKING HERE