What Is the Payout Ratio?
The payout ratio is a metric that can be used to assess the sustainability of a stock's dividend payments. In general, a lower payout ratio indicates that a company's dividend has room to grow and could withstand a drop in profits, while a high payout ratio could be a sign of an impending dividend cut.
Image source: Getty Images.
What is the payout ratio?
In a nutshell, the payout ratio is the percentage of a company's earnings that are paid out as dividends. Generally speaking, a lower payout ratio is better, as it means that the company's dividend has room to grow and could be sustained even if profits drop, but this isn't always the case.
Low payout ratios (or a complete lack of dividend payments) may indicate that the company prefers to use most or all of its profit to reinvest in its business, or to buy back shares. For example, if a company is growing rapidly, it may use most of its profits to build new factories or hire more employees. Or, if a company perceives its stock price to be inexpensive, then it may feel it's in shareholders' best interest to buy back shares instead of paying dividends.
On the other hand, a higher payout ratio may indicate that the company is mature, or is otherwise satisfied with sharing most of its profits with investors. As an example, AT&T is a relatively mature company and doesn't need to reinvest too much of its profits to sustain its business. For that reason, AT&T paid out 83% of its earnings over the past 12 months. While there is no set cutoff between a low and high payout ratio, a higher payout ratio is generally in the 50% to 90% range.
Finally, beware payout ratios that are near or above 100%. This indicates that the company is paying out more money as dividends than it is earning, which may be unsustainable and could lead to dividend cuts. One major exception is real estate investment trusts, or REITs. These companies required to pay out at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders, and "earnings" are not actually an accurate way to assess their profitability. Here's a primer on REIT profit metrics, but for the time being, just know that if a REIT's payout ratio is higher than 100%, that isn't necessarily bad.
How to calculate the payout ratio for your stocks
To calculate the payout ratio for your stocks, here's the general formula:
Generally, investors calculate the payout ratio over the period of one year (for example, when calculating the trailing-12-month payout ratio), but it can be done over any other period, such as quarterly.
For example, let's say one of your stocks had EPS of $2 in 2016 and paid out $0.50 per share in dividends. You would calculate its payout ratio like this:
How to use the payout ratio
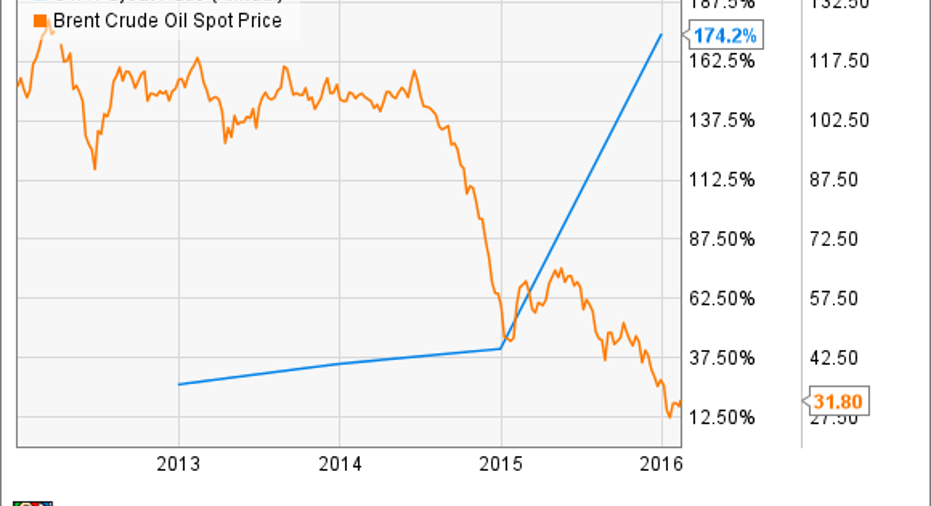
While it's certainly useful, the payout ratio doesn't paint a complete picture of the dividend's sustainability. For example, a stock that has a low payout ratio may also have a dangerously high debt load, a business that's vulnerable to recessions, or rapidly rising costs of doing business, all of which could threaten the dividend. As you can see in the chart below, this was the case with oil stocks such as Chevron. As oil prices collapsed in 2014 and 2015, Chevron's sub-30% payout ratio soared to more than 170% as profits fell.
CVX Payout Ratio (Annual) data by YCharts.
The bottom line is that the payout ratio is a great metric to use when evaluating dividend stocks, but it's only one piece of the puzzle that should be used as part of your due diligence before investing. You should incorporate several other metrics, such as these, into your analysis.
The $15,834 Social Security bonus most retirees completely overlook If you're like most Americans, you're a few years (or more) behind on your retirement savings. But a handful of little-known "Social Security secrets" could help ensure a boost in your retirement income. For example: one easy trick could pay you as much as $15,834 more... each year! Once you learn how to maximize your Social Security benefits, we think you could retire confidently with the peace of mind we're all after.Simply click here to discover how to learn more about these strategies.
This article is part of The Motley Fool's Knowledge Center, which was created based on the collected wisdom of a fantastic community of investors. We'd love to hear your questions, thoughts, and opinions on the Knowledge Center in general or this page in particular. Your input will help us help the world invest, better! Email us at knowledgecenter@fool.com. Thanks -- and Fool on!
The Motley Fool recommends Chevron. The Motley Fool has a disclosure policy.



















